What is a Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia happens when part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a muscle that helps you breathe. Normally, the stomach sits below this muscle. However, with a hiatal hernia, some of the stomach moves into the chest area. This can cause heartburn, chest pain, or trouble swallowing. Sometimes, people do not notice any symptoms. But for others, the symptoms can affect daily life.
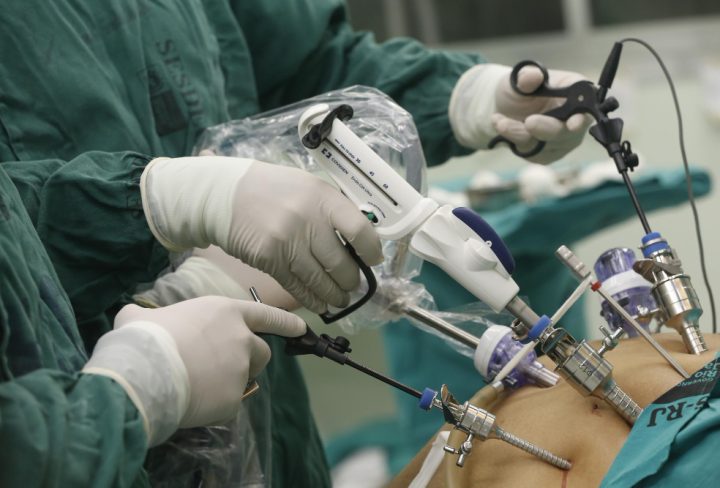
Overview of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery for hiatal hernia is a minimally invasive procedure. Instead of one large cut, the surgeon makes a few small cuts in the belly. Through these cuts, the doctor uses a thin tube with a camera, called a laparoscope. This tool lets the surgeon see inside the body on a screen. Because the cuts are small, recovery is often faster than with open surgery. Many people prefer this option for hiatal hernia repair.
Indications for Surgery
Not everyone with a hiatal hernia needs surgery. However, doctors may suggest surgery if:
Sometimes, surgery is the best way to prevent further problems. Your doctor will help decide if you need this treatment.
Step-by-Step Procedure
During minimally invasive hiatal hernia repair, the steps usually include:
Most surgeries take about 1 to 2 hours. Because the cuts are small, there is less pain and a lower risk of infection.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic hiatal hernia surgery offers many advantages. For example:
Because of these benefits, many people choose this minimally invasive option. According to the CDC, recovery is often quicker than with open surgery.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although laparoscopic surgery for hiatal hernia is safe, all surgeries have some risks. Possible complications include:
However, most people recover without serious problems. Your surgeon will discuss these risks before the procedure.
Recovery and Aftercare
After laparoscopic hiatal hernia surgery, most people go home within one or two days. During recovery, you may need to:
Usually, people return to normal activities in two to four weeks. If you notice fever, severe pain, or trouble swallowing, contact your doctor right away. For more recovery tips, the World Health Organization suggests following your care team’s advice closely.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
While not all hiatal hernias can be prevented, some lifestyle changes may help. For instance:
These steps can lower your risk of symptoms coming back after surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
For more information, consult a qualified anaesthesiologist or surgeon for personalized advice on laparoscopic surgery for hiatal hernia.